A Buyers Guide to 3D Scanning
3D laser scanners are a hot topic and 3D laser scanning is an advanced technology with a market growth forecasted by some reports to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% from 2021 to 2026. Other research indicates that the 3D laser scanner market will likely reach $16.66 billion by 2030.
What is a 3D laser scanner and what are they used for and as a company how do you choose the best 3D laser scanner on the market?
This article aims to give you the details on 3D laser scanning needed to help make an informed decision.
What is a 3D laser scanner?
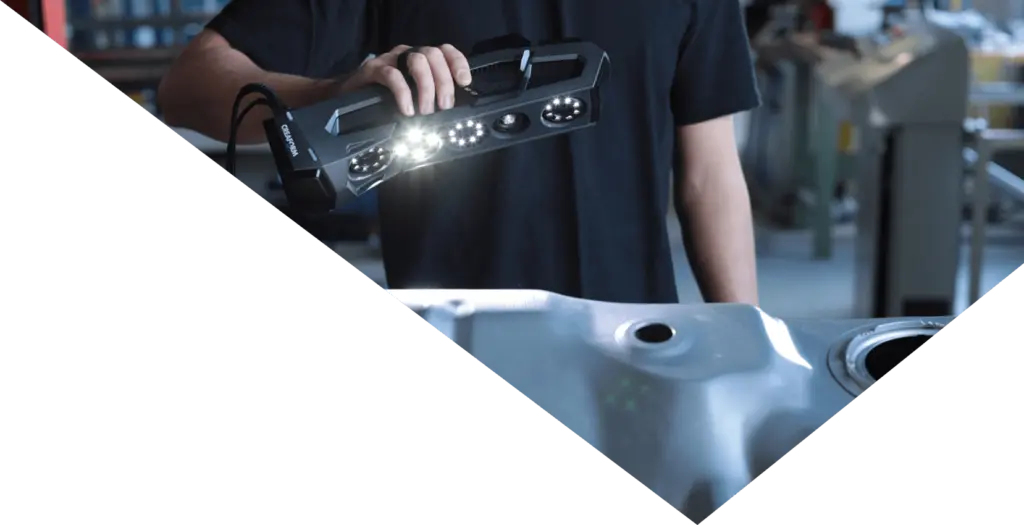
A 3D laser scanner is a non-contact and non-destructive device that digitally captures 3D measurements of objects and their surrounding environments using lasers. As a user scans an object, the 3D laser scanner projects a coded pattern of light from the lasers. This coded pattern will match the shape of the object to create a digital version of it.
The digital copy of the object can then be exported as a polygon mesh file, which is a representation of the 3D model, and used in different computer-aided design (CAD), inspection or 3D printing software.

What can a laser scanner do?
Depending on its brand, make and model, a 3D laser scanner can be used to scan all sorts of objects, regardless of the complexity of their geometries, shapes, size, material, and surface finishes, specialised 3D laser scanners can even scan human bodies and buildings!
Portable and handheld 3D laser scanners also enable operators to use them just about anywhere to acquire accurate 3D measurements no matter what the surrounding environment is like. Whether users need to scan a part on the production floor, a pipeline that has been excavated, or a hard-to-reach and ultra-small component in a vehicle, 3D laser scanners can generate the data required for further processing.
What industries use 3D laser scanners?

Where are 3D laser scanners used?
The most straight forward answer is…virtually anywhere! At their basic concept, 3D laser scanners contribute to creating 3D models (or replicas) of physical objects. Which means that professionals in a wide variety of sectors use 3D laser scanners, these can include but are not exclusive to:
- Aerospace
- Transportation and Automotive
- Consumer Products
- B2B Manufacturing
- Education
- Heavy Industries
- Healthcare
- Heritage, Art and Architecture
- Oil and Gas
- Power Generation
In addition, thanks to the democratisation of 3D laser scanning technologies, affordable and professional-grade 3D laser scanners are also accessible to hobbyists, artists, tinkerers, and everything in between. Check out some of the amazing projects that are carried out with more accessible 3D laser scanning solutions.
What is a 3D laser scanner used for?
Now we have identified which industries typically use 3D laser scanners, let’s explore the wide range of 3D laser scanning applications, including manufacturing. But don’t forget, 3D laser scanners are not just for production.
Here are some examples:
- Product Development & Design: 3D laser scanners can help engineers and industrial designers develop innovative new products, like high-performance street and off road sport motorcycles
- 3D printing (Additive Manufacturing): Design teams can quickly create prototypes of parts or complete products using 3D laser scanners and a 3D printer
- Reverse Engineering: Production teams use 3D laser scanners to reverse engineer critical parts for which they don’t have the original 3D models, such as in the automotive industry’s aftermarket
- Quality Control & Quality Assurance: Inspection teams leverage high-end 3D laser scanners to improve the quality control in additive manufacturing processes for large parts
- Maintenance, Repair & Overhaul (MRO): MRO professionals take advantage of 3D laser scanners to assess critical damage to aircraft components.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Carrying out inspections in nuclear power plants is facilitated by 3D laser scanners
- Science & Education: Researchers and professors are teaching the engineers and industrial designers of tomorrow how to use 3D laser scanners in their field of work
- Medical & Healthcare: Medical professionals and technicians use 3D laser scanners to create custom-moulded cranial remoulding orthoses
- Heritage, Archeology, Architecture & Art: Heritage and art preservation/archiving is simplified when restorers use 3D laser scanners
- Multi Media, Visual Effects & the Metaverse: 3D laser scanners are used to create non-fungible token (NFTs) for digital art and 3D models in the metaverse
- Building & Construction: The construction industry is increasing opting for 3D laser scanners for everything from validating design execution to creating building 3D models
What is the difference between laser scanning and fixed CMM scanning?

While there are a variety of 3D measurement solutions available on the market, there are two solutions that are often compared, these are portable 3D laser scanners and fixed coordinate measurement machines (CMMs) and both technologies feature the accuracy levels required for professional use.
A CMM is made up of a solid granite base table, gantry or bridge-mounted arm and a touch probe to be used for tactile measuring. It is often located in a laboratory or dedicated room because it can be very sensitive to ambient conditions, such as vibrations, dust, humidity levels, etc. The main advantage is that a CMM is highly accurate; however, it needs to be operated by an experienced metrologist, it can be slow, and is limited in flexibility. Parts need to be carried to the CMM, which makes it inefficient for accelerated throughput and difficult to use for large parts.
Portable 3D laser scanners are, in general also very accurate. Depending on the brand and model, they are fast at acquiring 3D measurements. What’s more, thanks to their intuitive interfaces and ergonomic designs, they are easy to use by operators with varying skill levels. Also, because they are portable and robust, 3D laser scanners can be used on the shop floor or outside; they can withstand harsh conditions without sacrificing data accuracy, reliability, and repeatability.
Quite often as an example, manufacturers will invest in both technologies. They will use the CMM for only the most important inspections that require the highest level of accuracy and then 3D laser scanners are used for all other 3D measurements, eliminating bottlenecks at the CMM and improving overall productivity.
How much does a 3D laser scanner cost?
The price range of 3D laser scanners is heavily dependent upon the quality and performance levels of the devices.
Cheap 3D laser scanners can be acquired for less than £1,000. Medium-price 3D laser scanners can hover in the tens of thousands and Metrology-grade 3D laser scanners, especially those used for automated quality control, Industry 4.0 processes, and critical product design applications with extremely tight tolerances and strict standards, can be priced at over £80K.
More often than not, companies don’t want to risk the significant operational costs and substantial business damage that can be caused by using below-par 3D laser scanners.
Here are some instances of why using a low-cost 3D scanner in professional applications could be a huge mistake.
- Performing inspections on aircraft components with a 3D laser scanner without the right accuracy levels could prove fatal for passengers in the event of a crash.
- During NDT assessments on oil and gas pipelines, inaccurate data can mean inspectors may not detect potential damage, like cracks and corrosions, that can cause catastrophic failures that put the surrounding population and environment in danger.
- Imagine if quality control teams on a manufacturer’s new vehicle miss defects in its sub-assemblies, which later on entails an extensive and costly car recall.
You can read this article for more information on the problems associated with low-cost 3D laser scanners for professionals here.
How to choose the best 3D laser scanner on the market
Selecting the right 3D laser scanner for your specific application depends on many different factors.
What are the things that you should consider when choosing a professional metrology grade3D laser scanner?
Make sure you take the following criteria and functionality into consideration when purchasing a 3D laser scanning system:
- Accuracy and repeatability: How accurate do you need the 3D laser scanner to be? Does your application require high tolerance levels or compliance with stiff norms? If so, you will want to gain peace of mind knowing the 3D laser scanner you opt for generates accurate and repeatable results.
- Resolution: In terms of resolutions, the quality of the scan data output will probably be important if your application entails making assessments with a high level of detail. The higher the resolution, the more detail there is on the 3D model.
- Speed: Is team efficiency critical? Are you designing a product that must have a fast time to market? Low-cost 3D laser scanners can take much more time to capture data than professional 3D laser scanners.
- Ease of use: Some 3D laser scanner technologies are easier to use than others. Be sure to test drive how intuitive and ergonomic each 3D laser scanner is. The last thing you want is for your team to be bogged down by complicated setups and use.
- Part size: Do you normally take 3D measurements on small parts, large parts, or components of all sizes? The specs of 3D laser scanners should inform you of the range in sizes, either in mm, cm or m (in or ft).
- Portability: Just how portable is the 3D laser scanner you are evaluating? True portability comes from not having to use an external positioning device. A 3D laser scanner should be completely standalone so that it can be used on a shop floor, for fieldwork, or in unstable/uncontrolled/tight areas. You can read more about the importance of portability in 3D laser scanning technologies here.
- 3D laser scanning software: Not all manufacturers provide integrated 3D software platforms that work seamlessly with their 3D laser scanners. This type of software features various modules or functionalities, including facilitating the transition between the scan data to CAD software and accelerating dimensional inspections. You get the most out of your 3D laser scanner with software that takes the post-scanning process to a whole new level.
- Training, support, and maintenance: Investing in a 3D laser scanner should also include carefully determining the level of localized training, support and maintenance services the manufacturer offers. Quality and high-end 3D laser scanner manufacturers back their devices with a stellar after-sales service, either directly through them or their network of certified distributors.