The definition of metrology is “the science of measurement, embracing both experimental and theoretical determinations at any level of uncertainty in any field of science and technology” according to the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM, 2004).
At its core, metrology is the study and application of measurement. Its primary aim is to ensure consistency, reliability, and accuracy in all forms of measurement, spanning from simple length measurements to more complex quantities like electrical current or temperature. This ensures that products and processes across various industries are standardised, safe, and of high quality.
The science of measurement spans from simple tape measures and distance to the measurement of atoms on a microscopic level. Refined metrology instruments are so sensitive that humans cannot be in the same room as measurements are being taken as our body heat alone can affect and tamper with results.
Industrial Metrology Ranges
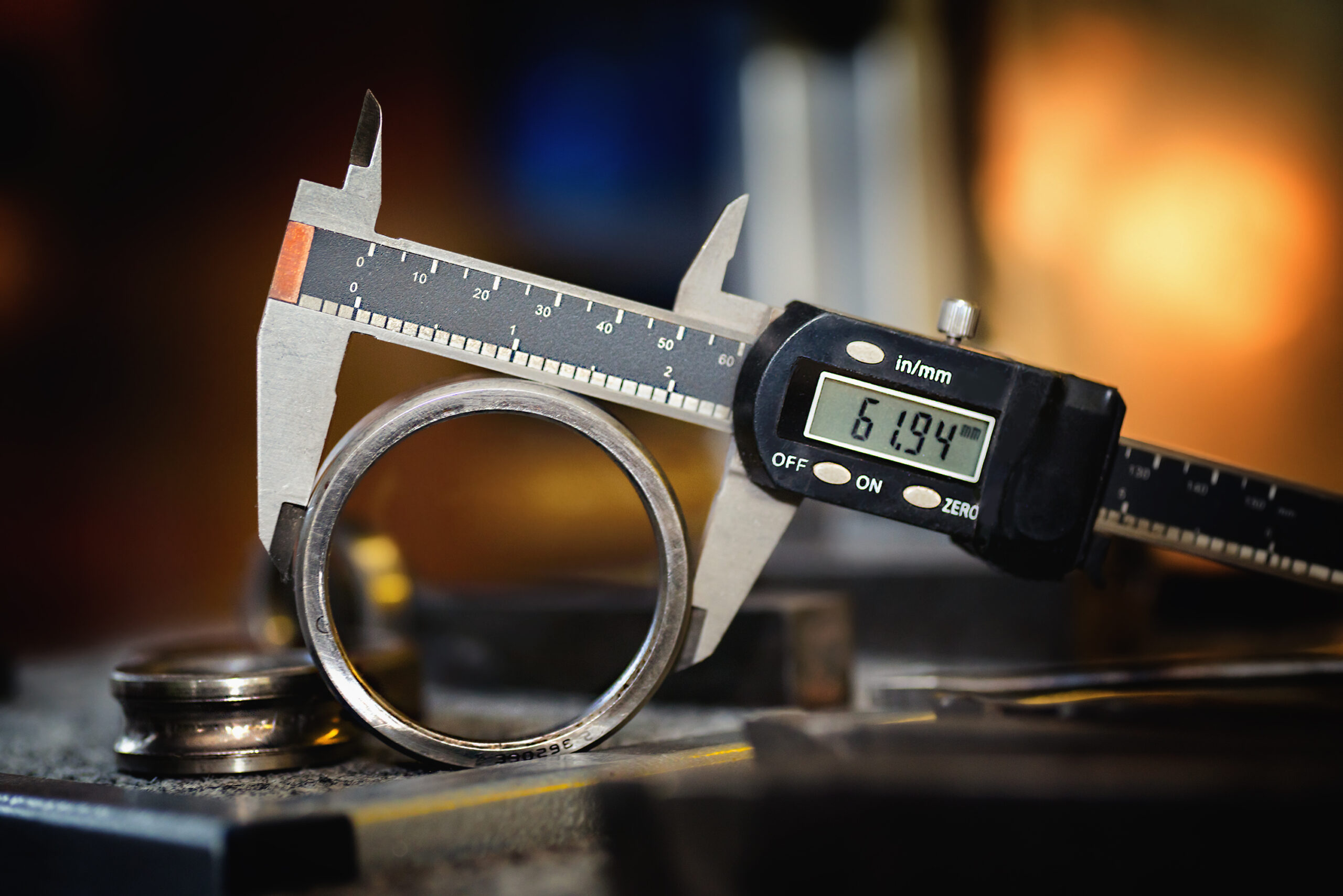
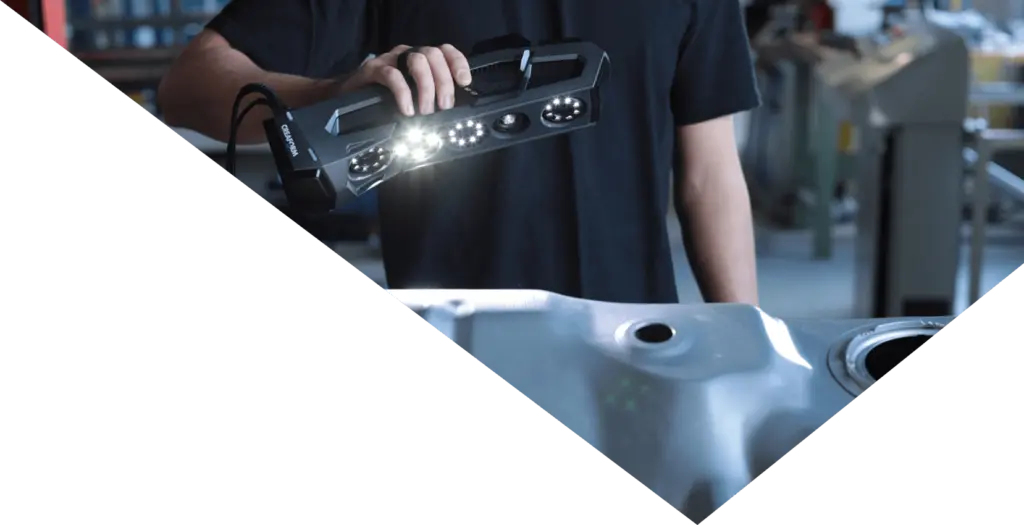
At Measurement Solutions, our industrial metrology 3D scanning and CMM machines measures up to an accuracy of 0.025mm and can take up to 1.8 million measurements per second. This opens up range of opportunities manufacturers to significantly increase speed and effectiveness throughout the process from design manufacturing and inspection.
Thanks to the advancement technology, and the growth of industries previously unavailable to us, the need for precision and complex measurements has arisen. Due to this, metrology has ben divided into 3 categories. These are:
- Scientific metrology
- Applied metrology
- Legal metrology
Scientific Metrology
Scientific metrology focuses on creating new measurement methods and establishing measurement standards. National labs, such as NIST (USA) and Inmetro (Brazil), coordinate these efforts, with international alignment by the BIPM. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and groups like VAMAS further standardise practices, aiming to facilitate trade in high-tech products by setting guidelines and specifications for advanced materials.
Applied Metrology
Also known as industrial metrology and technical metrology. Applied metrology covers the application of measurement to a multitude of industrial processes. Whether that be manufacturing, automotive, aerospace and much more. Industrial metrology ensures the measurement systems are calibrated, suitable and under quality control. Applied metrology can be summed up to everything that ensures that
Legal Metrology
Legal metrology is the EU legislation on measuring standards. This legislation is often seen as the standards for market goods or services. There are many daily examples of this practice that we take for granted. For example, we use weight as a measurement when we purchase foods such as vegetables, meat and fish; we use time as a measurement for services, appointments and travel, and we use volume for drinks and fuel.
The global standards for legal metrology legislation is the OIML.
The Future of Metrology
The incessant march of technology ensures that metrology remains a dynamic field. With the rise of industries such as nanotechnology and biotechnology, there’s an ever-growing demand for more advanced metrology equipment. Additionally, as global industries become more interconnected, the need for standardised measurements becomes more paramount.
Also, with the emergence of concepts like the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart manufacturing, the realm of metrology is set to expand even further. We can anticipate more integration of metrology devices with digital platforms, enabling real-time monitoring and feedback in industrial processes.
If you have found this article of interest, we suggest you look through our other material here. If you would like to find out more about any of our Creaform 3D scanners, you can either contact us or book a demo.