The Impact of 3D Scanning on Automotive Production Line Efficiency
In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, technological advancements continually reshape industry practices. One such innovation, 3D scanning, continues to develop as a tool for transformation in the automotive sector.
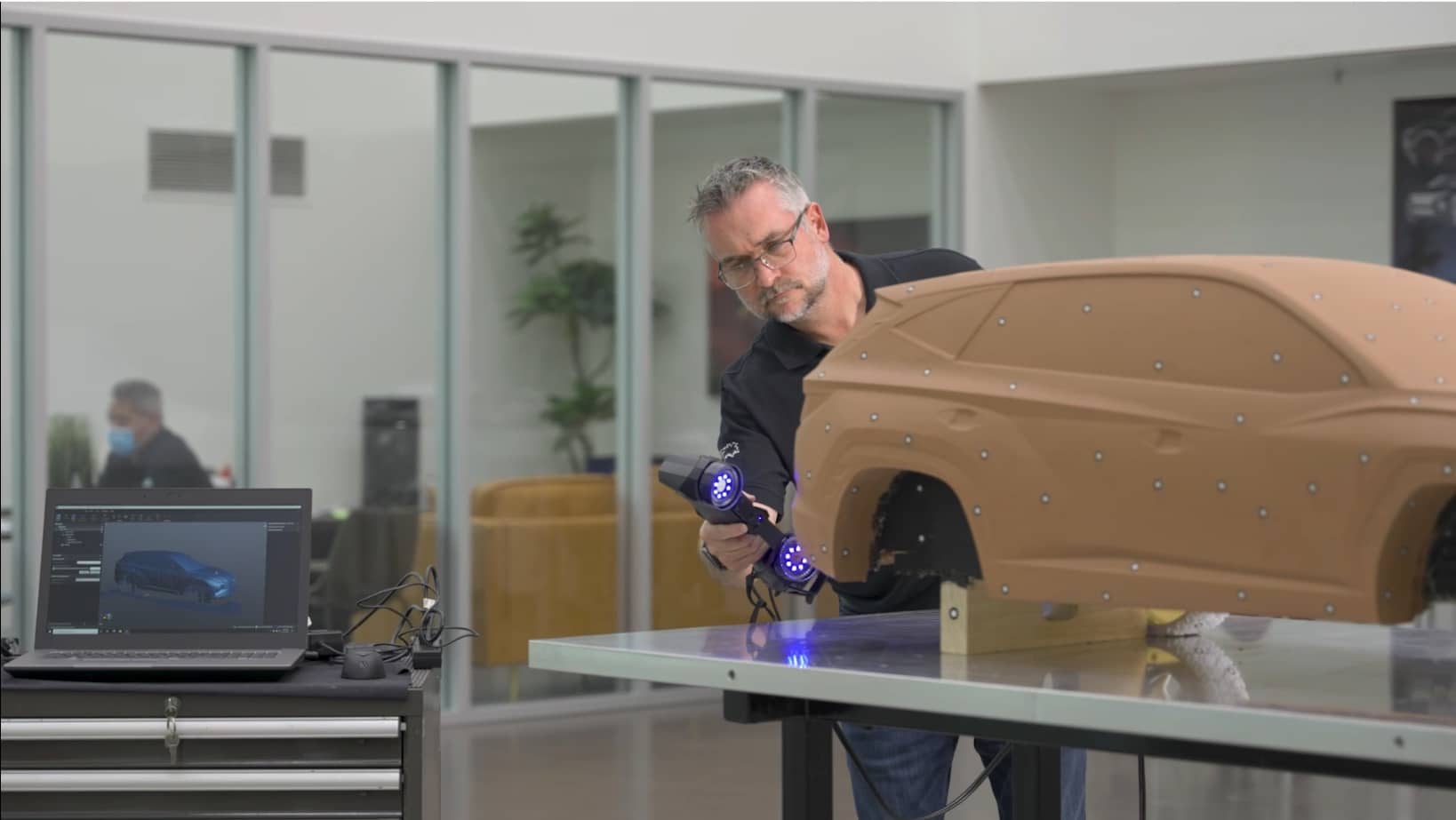
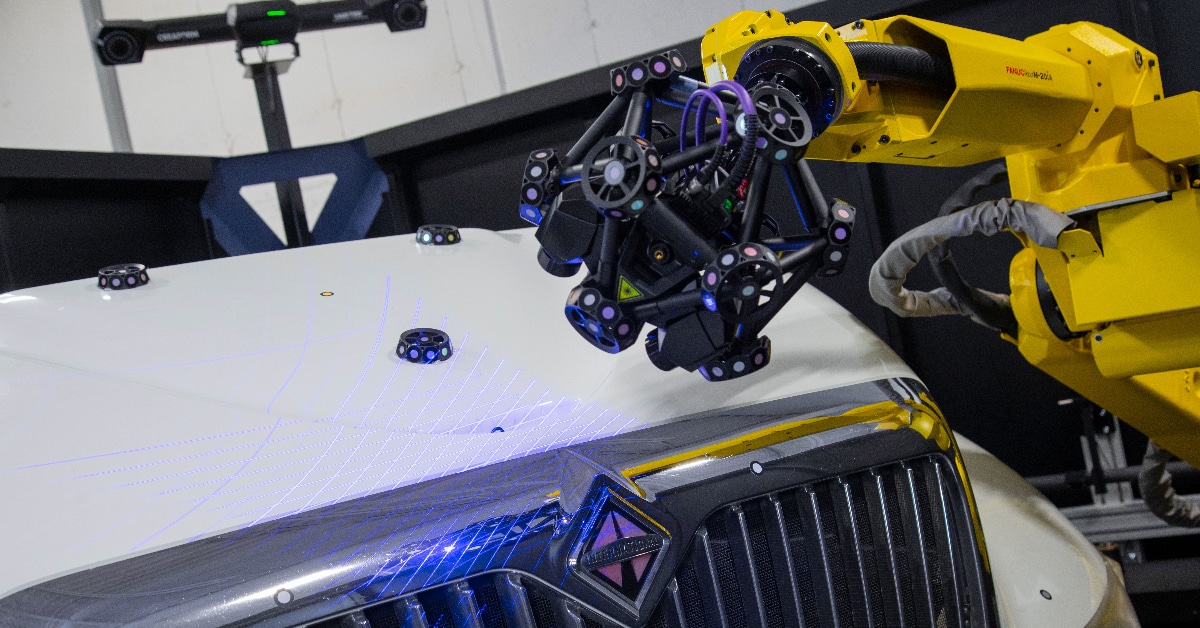
Traditional manufacturing processes often involve manual measurements, templates, and moulds, which can be time-consuming and leave the possibility for human errors. However, with the integration of 3D scanners into the manufacturing process, production lines are experiencing a revolution in efficiency and accuracy.
The Evolution of Manufacturing in the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has always been at the forefront of innovation. From Henry Ford’s assembly line to the modern automated robotics, the industry constantly seeks innovative ways to enhance production efficiency and reduce costs. 3D scanning is the latest addition to this list of innovations, offering a non-contact method for capturing the intricate details of physical objects. This technology is proving to be a game-changer, particularly in the context of automotive manufacturing.
Benefits of 3D Scanning in Automotive Production
1. Precision and Accuracy
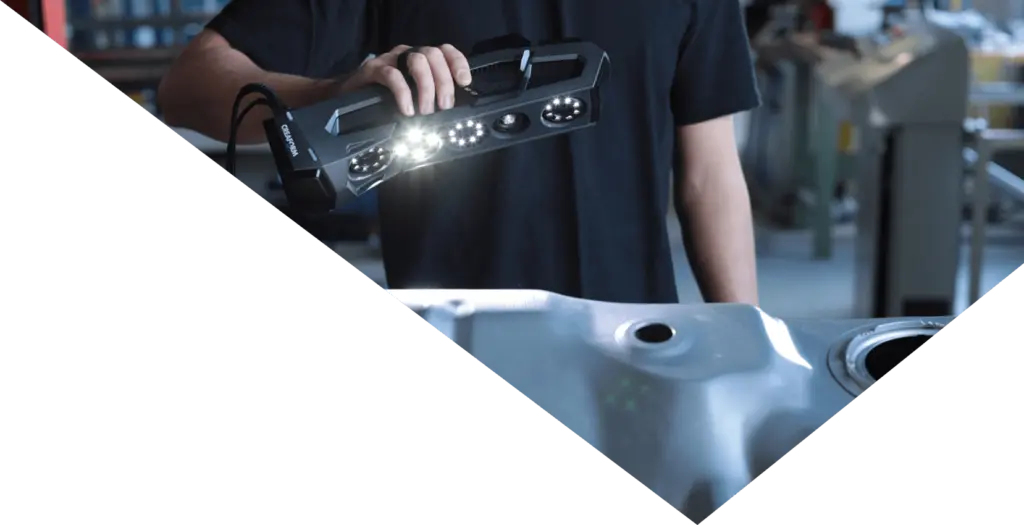
Traditional measurement methods often result in small discrepancies that can accumulate during assembly, leading to compromised quality. 3D scanning eliminates this issue by capturing precise measurements of even the most complex parts, ensuring a higher level of accuracy in the final product.
2. Time Efficiency
3D scanning significantly reduces the time required for measurement and analysis. What used to take hours or days can now be completed in a matter of minutes, allowing manufacturers to accelerate their production cycles and respond more swiftly to market demands.
3. Quality Control
With real-time and highly detailed scans, manufacturers can detect defects or imperfections early on in the production process. This proactive approach to quality control helps prevent costly recalls and ensures that only products meeting the highest standards reach consumers.
4. Customisation
Automotive manufacturers are increasingly offering customisable features to meet individual customer preferences. 3D scanning facilitates the integration of these customised components seamlessly into the manufacturing process.
5. Reverse Engineering
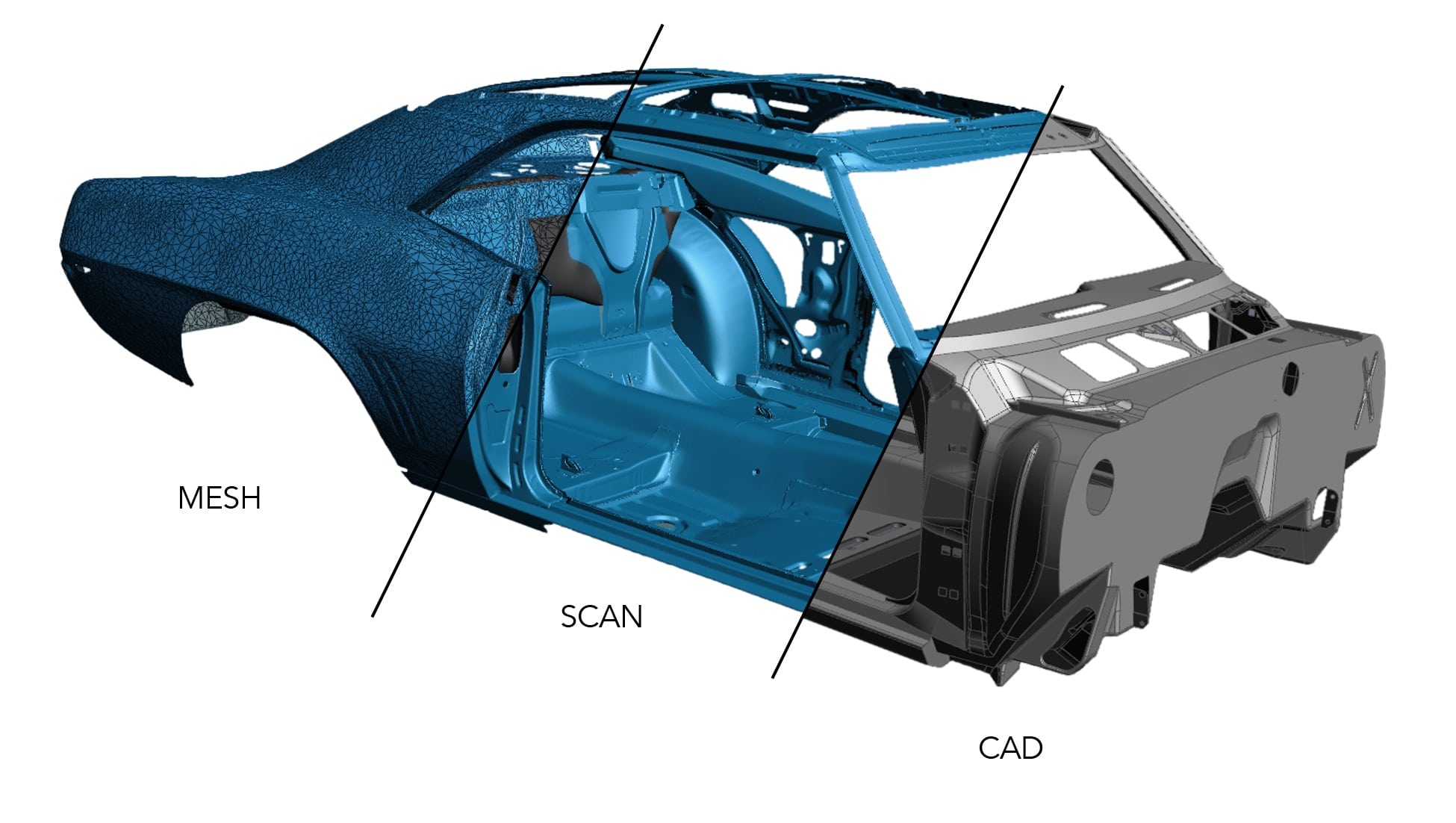
When developing new models or improving existing ones, 3D scanning enables reverse engineering. Manufacturers can scan existing components, analyse their structure, and create digital models for further modifications, allowing for innovation, rapid prototyping and highly accurate parts.
6. Rapid Prototyping
3D scanning complements rapid prototyping techniques such as 3D printing. Once a digital model is created through scanning, it can be easily 3D printed to create physical prototypes for testing and validation. This accelerates the product development cycle and reduces overall costs.
7. Reduced Waste and Costs
With accurate 3D scanning data, manufacturers can better manage their inventory and production, reducing waste and optimising material usage. This ultimately leads to cost savings and more environmentally friendly practices.
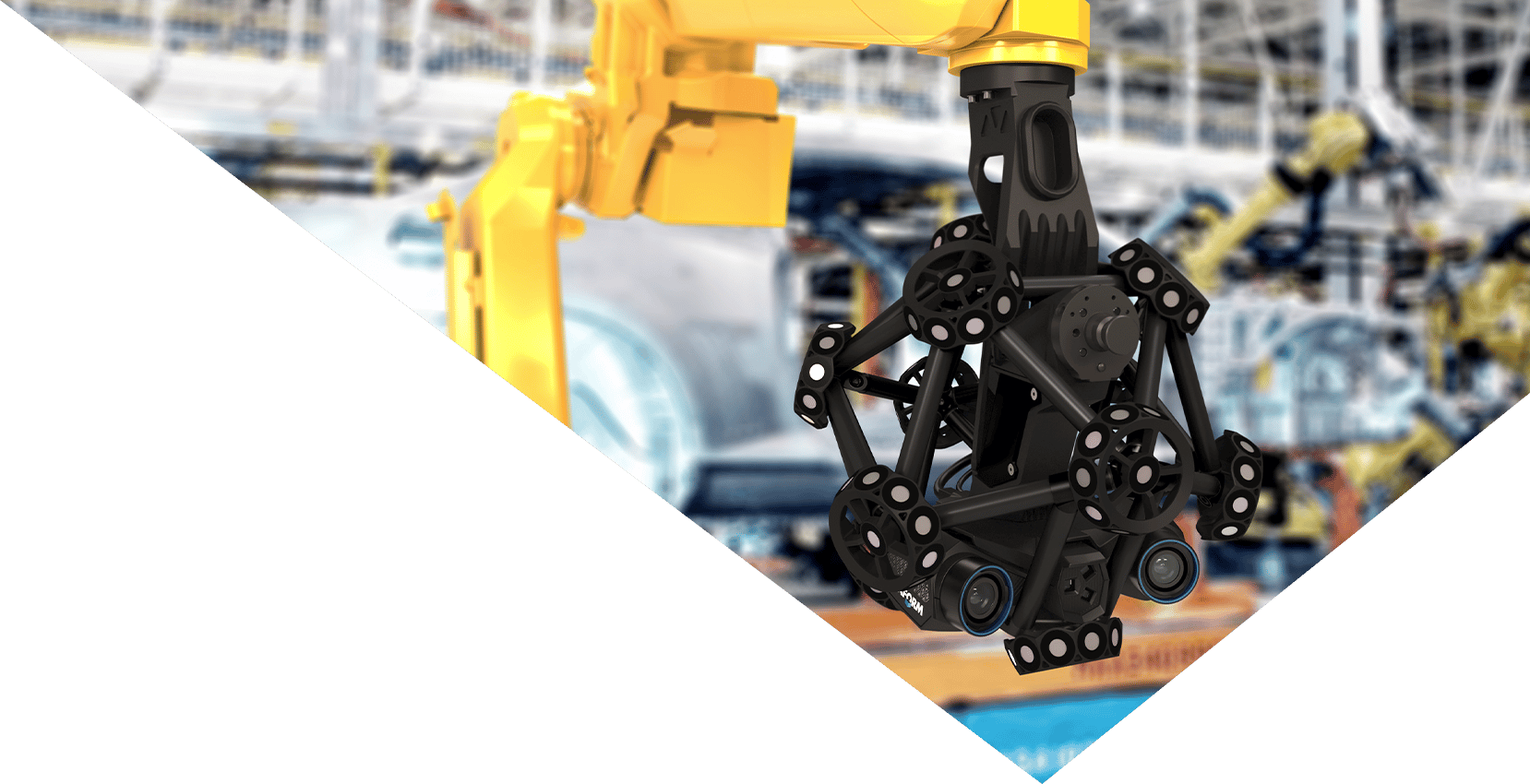
Applications of 3D Scanning in Automotive Manufacturing
1. Design and Development
During the design phase, 3D scanning helps capture real-world data that can be used to create digital prototypes. This enhances collaboration between design and engineering teams, reducing the need for physical prototypes and minimising design iterations.
2. Tooling and Moulding
Creating moulds and tools for automotive parts traditionally involves manual measurements and adjustments. 3D scanning streamlines this process by providing accurate measurements for tooling and moulds, resulting in better-fitting parts and reducing production bottlenecks.
3. Quality Inspection
Traditional inspection methods involve sampling parts for measurement, which might not catch every defect. 3D scanning allows for comprehensive inspections, ensuring that every part can be scrutinised for accuracy, catching more defective products and preventing downstream delays.
4. Aerodynamics Analysis
You can capture the exact shape of a car’s exterior with 3D Scanning, including intricate details like spoilers, vents, and grilles. This data is crucial for aerodynamics analysis, helping engineers optimise the vehicle’s airflow to improve fuel efficiency and performance.
5. Crash Test Simulation
Obtaining precise measurements of vehicles involved in crash tests is simplified with 3D Scanning and the data is vital for simulating and analysing crash scenarios, helping to develop safer vehicle designs and meet regulatory standards.
6. Aftermarket Parts
The automotive aftermarket is a significant industry in itself. 3D scanning facilitates the production of replacement parts by capturing the dimensions of original components. This is particularly valuable for older car models where traditional moulds might be unavailable.
7. Virtual Showrooms and Online Configurators
In the digital realm, 3D scanning allows automotive manufacturers to create virtual showrooms and online car configurators. Customers can interact with lifelike 3D models of vehicles, customise their features, and visualise their choices before making a purchase.
These are just a few of the applications that demonstrate how 3D scanning technology has become an indispensable tool in the automotive industry, enabling innovation, improving efficiency, and enhancing the overall customer experience.
If you have found this article of interest, then we would suggest that you look through our other material here. If you would like to find out more about any of our Creaform 3D scanners, you can either contact us or book a demo.